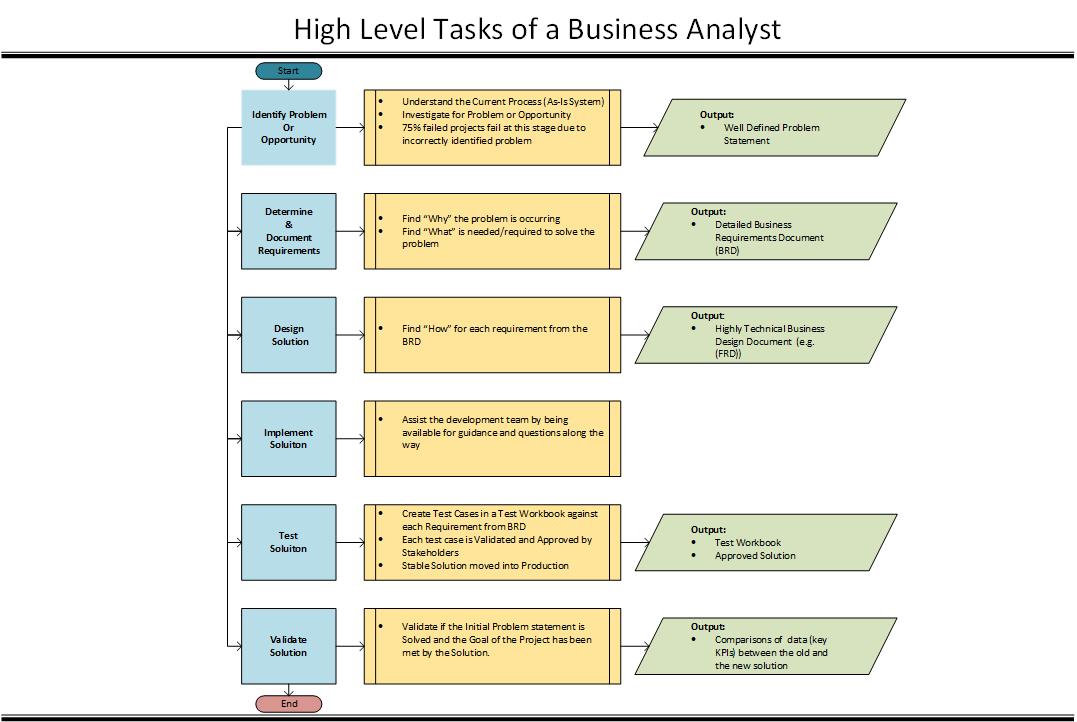
High-Level Tasks of a Business Analyst
- Step1: Identify Problem or Opportunities
- Step 2: Determine and Document the Requirements
- Step 3: Define/Design the solution that best achieves the requirements
- Step 4: Implement the Solution
- Step 5: Test the Solution
- Step 6: Validate the end result solves the original problem
Step 1: Identify problems or opportunities
Problems could be:
- Identifying a way to get efficiency in a project
- Identifying a change to be made due to a regulation
- Identifying a new software feature that would make life easy for the end-user
- Etc
75% of failed projects fail at this stage
Incorrectly identified problems make the solution that is determined null and void and causes a huge waste of time and resources.
Once the BA thinks the problem is identified, he/she must validate the problem statement with the project team and ensure everyone is in agreement.
Output – Problem Statement
Step 2: Determine and Document the Requirements
Once the problem is identified, it must be solved.
For this you have to answer these 2 questions:
- Why is the problem occurring?
- What is “needed/required” to be done to solve the problem?
The BA has to be factual and quantitative about what would be accomplished. Hence he/she figures out what the business is looking to accomplish and the individual user needs.
This is done by eliciting and documenting what is “needed” or “required” to solve this problem.
The BA should never “guess” or “assume” what is needed/required even if it is trivial. He/She should always have a need/requirement approved by stakeholders.
Output: Detailed Business Requirement Document
A BRD states what would be accomplished at the end. It is a list of all the requirements of the individual users. It defines once all the needs/requirements are met what would be achieved.
Step 3: Define/Design the solution that best achieves the requirements
After all the requirements have been identified, documented, and approved, the BA designs the solution.
For this the BA:
- Dives deep into the BRD – the What.
- Identifies how each of those requirements could be met – the How
Output: Highly Technical Business Design Document or something similar e.g. Functions Requirements Document (FRD). It goes through how the solution would be constructed.
Step 4: Implement the Solution
The BA takes a step back and helps the development team to build the solution. He/She is available for any assistance that they need.
For software projects, the solution should be implemented in a test environment and not in a production environment.
The test environment is a replica of the production environment and any change made to it doesn’t affect the production. Hence major changes and adjustments can be done in it without worrying about causing downtime to users.
Step 5: Test the solution
Once the solution is implemented it is time to test it. The BA verifies if the identified business requirements have been met.
The BA goes through each requirement from the BRD and validates that each of them is accounted for in that final solution.
Simultaneously he/she documents the test results in a Test Workbook.
Once each Test Case from the test workbook is verified the BA hands over the test workbook to the rest of the project members for them to verify that each of the requirements is met.
The approved solution is pushed to the production environment.
All the necessary training is also conducted for the users of the solution. A Business Analyst may or may not conduct the training however he/she is usually the person to create the training documents.
Output: A completed testing document and an approved solution.
Step 6: Validate the end result solves the original problem
Validate if the initial problem statement and the goal of the project have been met by solution.
Example to understand the High-Level Tasks of a Business Analyst
Let us assume you are hired by a fictitious company ABC Corp, that wants to improve the efficiency of their lead management process.
Step 1: Identify Problem or Opportunity
You begin by having a discussion with the company staff to understand the current process.
Below are your findings from the discussion:
- They have a Web Portal for lead inquiry management.
- The Lead performs the following activity on the portal
- Enter their contact details
- Place an inquiry for products or services
- The Portal triggers a process to automatically send an email to a group of admins
- The Admins have to manually enter the lead details into a CRM software
- Once the lead is created in the CRM software the concerned Sales Rep gets a mobile notification and they can contact the lead immediately.
Once you’ve understood the current process you further investigate it to figure out a problem or opportunity, if any.
In ABC Corp’s case there is a problem.
On many occasions, the lead would request info not just from ABC Corp but also from their competitor. You discovered this through the following fact that came up during the discussion with the staff:
By the time, the ABC Corp’s Sales Rep contacted the lead, the lead was already in touch with the competitor and a few times had also already purchased from the competitor.
As a result, the web-generated leads (which are warm leads and hence should have high conversion ratio) had poor conversions.
After the analysis of the entire process, you prepare the following problem statement :
ABC Corp is losing sales from its website-generated leads because their competitor can contact the leads faster.
Step 2: Determine and Document the Requirement
In this step you find:
- “Why” the problem is occurring
- “What” is needed/required to solve the problem
First, you find “why” the problem is occurring.
For this you
-
- Document the current system
- Perform analysis on it to identify the root cause
Document the current Lead Management process (As-Is system).
The combination of people, process, data and technology that form the current system is documented.
-
-
-
- People:
- Identify various stakeholders (people affected by / involved in the system/project).
- Process & Technology:
- Website team – Builds and Manages the Lead Management Web Portal
- CRM Administrators – They manually create the leads in the CRM system.
- Field Sales Reps – They receive notification from CRM and contact the Leads.
- Data:
- Data from each group is collected and detailed process flow of the current system is mapped.
- People:
-
-
Perform an analysis of the detailed process flow of the current As-Is system to identify the flaw in the process/system.
The following flaw in the system is identified:
The CRM admins have to “manually” enter the lead info in the CRM software and this slowed down the whole process drastically. This was because the lead volume is high with respect to the admin count and also admins had additional duties. As a result, they couldn’t enter the leads into the system efficiently.
The time between lead inquiry on the website and the sales rep receiving the lead notification – 8 hours.
Second, you find “What” is needed/required to solve the problem
By now you have fully understood the “why” of the problem and now you have to find “what” needs to be done to solve it.
You had a meeting with the project staff and understood that to solve the current problem the delay between the lead inquiry submission on the web portal and the lead creation in the CRM system should be reduced.
After careful discussion the acceptable delay was agreed to be 15 mins.
You document this requirement along with other requirements formally in a BRD. After everything is documented you have to get signed approval from the concerned stakeholders that everything is accurate and nothing is missing.
Step 3: Design the solution
By this time you know the “exact” problem that needs to be solved. In this step, you determine “How” you’ll solve the problem.
The key thing you want to solve – How to create leads in CRM in 15 minutes from the time they are submitted on the website.
You come up with two viable solutions to solve the problem:
- Solution one:
- Make it mandatory for admins to enter leads the moment they get the email from the portal.
- Solution two:
- Create a system for direct integration of the website with the CRM software.
You perform analysis on the pros and cons of both the solutions, to figure out your recommended solution.
Below are your findings:
Problem with solution one:
-
-
- Based on the current volume of leads the company will have to hire more admins.
- Also, If the lead volume went further up then this approach will not be scalable as hiring more admins will add to an additional cost which will reduce the profits from the additional leads. And if the lead volume fell again then the additional admins will add to the cost.
-
Advantages of solution two:
-
-
- Leads can be created in CRM in real-time.
- No need for additional admins.
- Highly scalable if the volume of leads increased.
-
Based on the above analysis, Solution Two is selected as your recommended solution to be implemented.
Once the solution is identified then all the technicalities of implementing the solution is worked out. The details are captured in a detailed design document.
Step 4: Implement the solution
A software development team would implement your recommended solution.
The following tasks are done by you in this phase to bring the software development team up to speed:
- Explain to them the initial problem
- Explain to them the requirements to solve the problem
- Explain to them the chosen solution
- Explain to them the project documentations
Once the development begins, you assist the development team by being available for guidance and questions along the way.
Step 5: Test the solution
In this phase you go through each requirement from the BRD and prepare test cases against each of them in a test workbook.
Each test case validates if the requirement from the BRD is solved in the solution
Thorough testing is done by various stakeholders. This is a cyclical process between the testing team, the development team, and other stakeholders. All the defects are resolved and the software is stabilized.
Once the software is stable and approved by the concerned stakeholders:
- The users are trained on the software and the new process
- The software is moved into the production environment.
Step 6: Validate the end result
After a few weeks of implementation of the new solution you perform analysis on the new solution and check if the original problem statement is solved.
The following data was gathered for the ABC Corp:
The leads were created on an average of 20 seconds from the time they were submitted on the web portal. This was exceptionally better than the planned 15 minutes.
When the lead was created on a working business day, the field sales rep could reach the lead in less than 30 minutes. This greatly improved the conversion ratio from 8% to 24% and generated additional revenue of 100 thousand dollars in just 3 weeks.
Congratulations! The project exceeded the expectations and was a grand success 🙂
The post is based on my notes and understanding from this BA tutorial